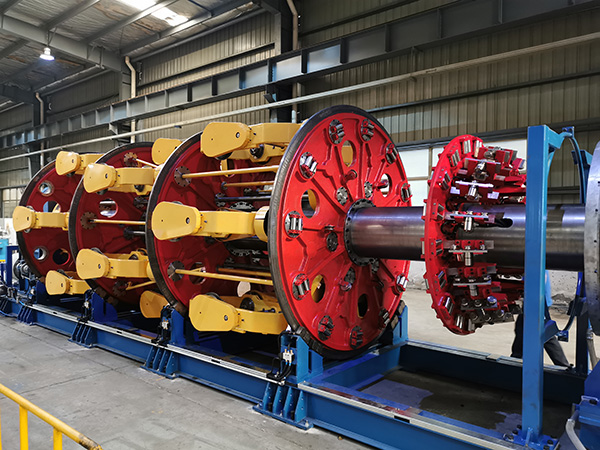
Products
China New Product Phosphate Treatment For Steel Wire - Steel mesh skeleton polyethylene pipe – Fasten
China New Product Phosphate Treatment For Steel Wire - Steel mesh skeleton polyethylene pipe – Fasten Detail:
Application
In the past 20 years, new plastic pipes have been widely used in municipal, gas and power plant water intake fields. Especially with the continuous optimization and innovation of polyethylene polymerization technology, there are increasingly higher tensile strength polyethylene materials. To further broaden the range of pressure levels for plastic pipes, especially in recent years, through the research of interdisciplinary technology, the steel-plastic composite technology introduced has successfully solved the problems of polyethylene (PE) pipes in terms of pressure level, anti-corrosion, and effective circulation diameter. Used in a wider range of fluid transportation applications.
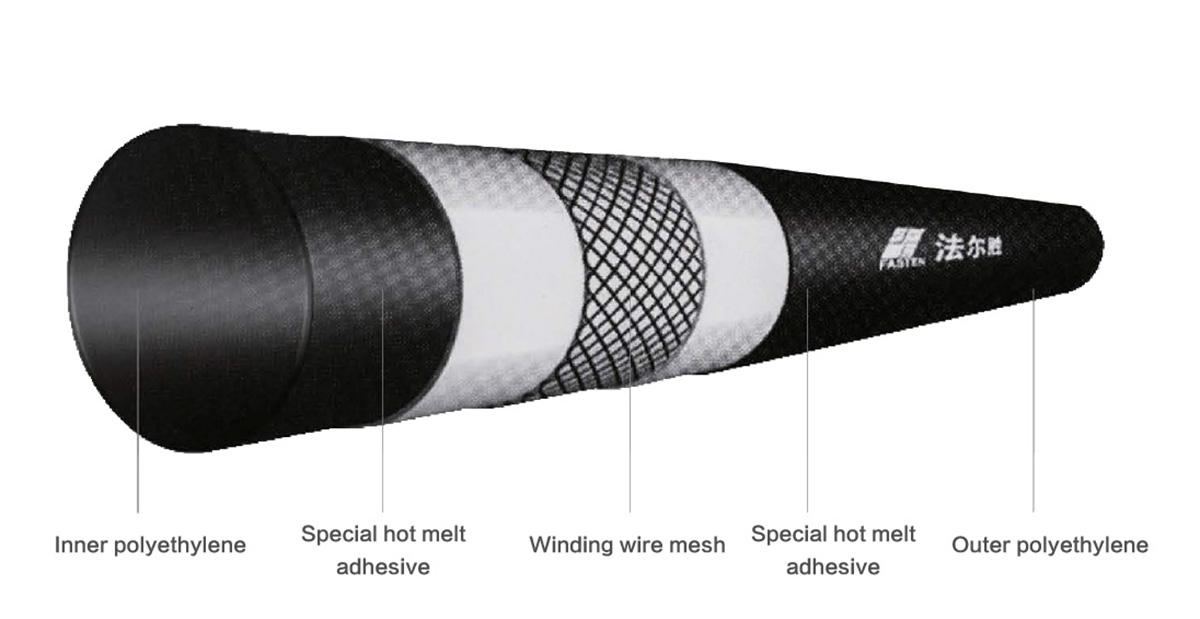
Structure: This product is a reinforced frame with a core layer of continuously wound high-strength steel wire after coating treatment, and a special hot-melt glue and plastic are combined into a whole pipe by extrusion molding method.
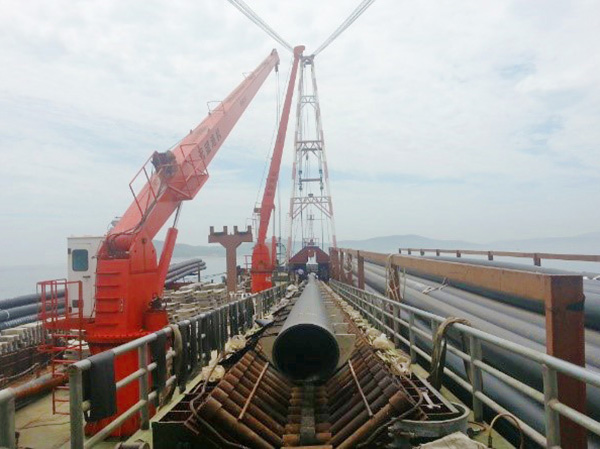
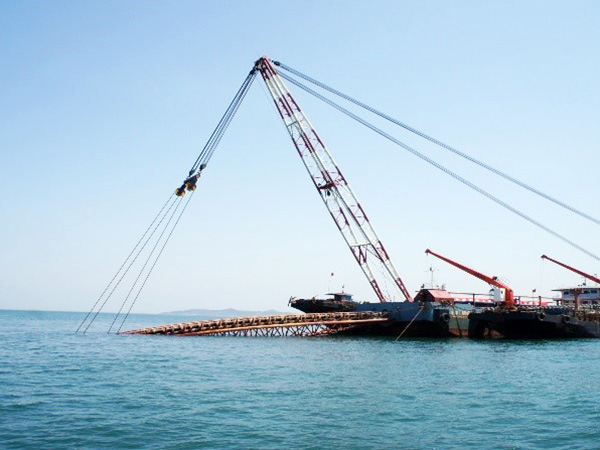




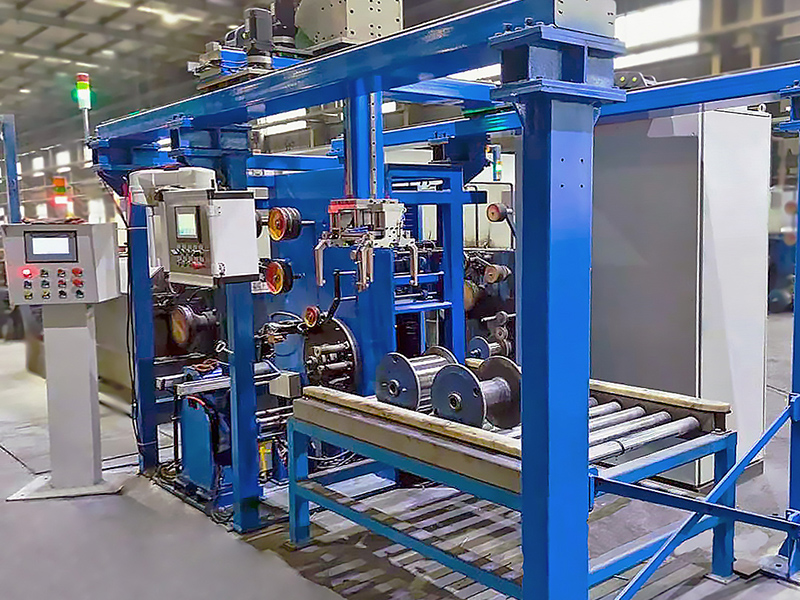
Features
Economic performance of the pipeline
Using high-density polyethylene as the inner and outer layer materials, the steel mesh skeleton polyethylene plastic composite pipe has the excellent performance of polyethylene pipe products. Due to the effect of the steel skeleton, the composite pipe of the same pressure level has а smaller wall thickness than pure plastic pipes. The effective circulation агеа is larger, and the good corrosion resistance and wear resistance ensure that the service life of the pipe сап bе as lang as 50 years, which effectively improves the economic performance of the pipeline.
Strengthen the skeleton to effectively suppress cracks
The use of а high-strength steel mesh core layer as а reinforcing skeleton effectively inhibits the chronic crack production and rapid crack propagation of polyethylene materials, and has higher compressive strength (the nominal pressure of the water pipeline reach З.5МРа) and stranger сгеер resistance, Higher impact resistance, and its performance indicators аге superiority polyethylene pipes.
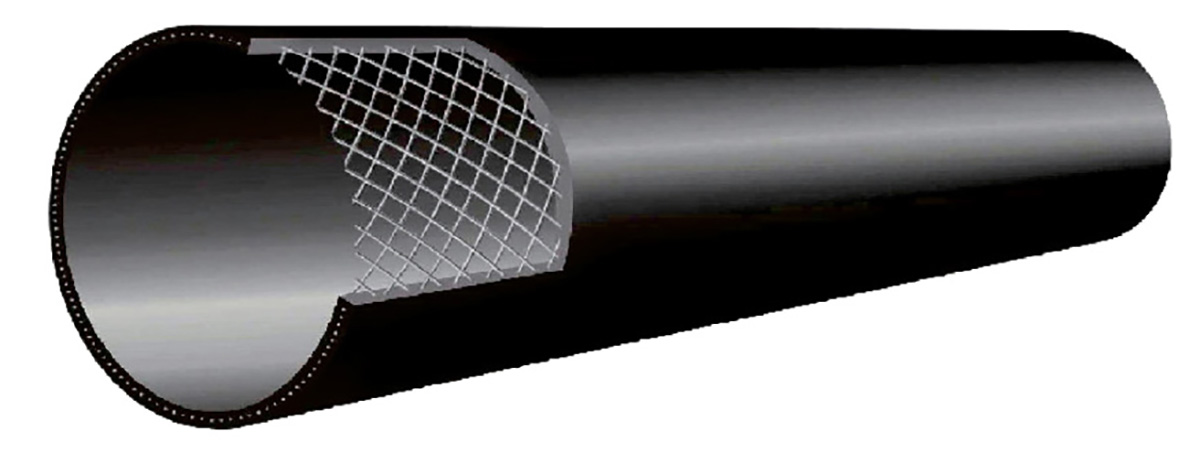

Technical Parameters
| Absolute roughness table of inner wall equivalent of various pipes | |||
| Type of pipe | Value mm | Type of pipe | Value mm |
| New seamless steel pipe | 0.04-0.17 | New cast iron pipe | 0.2-0.3 |
| Steel frame plastic composite pipe | 0.0015-0.009 | Old cast iron pipe | 0.5-0.6 |
| Copper pipe in general | 0.19 | Galvanized steel | 0.152 |
| Old steel pipe | 0.60 | Reinforced concrete pipe | 1.8-3.5 |
|
Nominal outer diameter |
Average outer diameter |
Minimum nominal wire diameter |
Nominal pressure |
|||||
|
Dn(mm) |
Allowable deviation |
Mm |
0.8 |
1.0 |
1.6 |
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.5 |
|
Nominal wall thickness en and allowable deviation of wall thickness ey at any point/mm |
||||||||
|
50 |
+1.2 0 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
5.0 |
5.5 |
6.0 |
6.5 |
|
63 |
+1.2 0 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
5.5 |
6.0 |
6.5 |
7.0 |
|
75 |
+1.2 0 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
6.0 |
6.5 |
7.0 |
7.0 |
|
90 |
+1.4 0 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
6.5 |
7.0 |
7.5 |
8.0 |
|
110 |
+1.5 0 |
0.5 |
- |
6.0 |
7.0 |
7.5 |
8.0 |
8.5 |
|
125 |
+1.6 0 |
0.6 |
- |
6.0 |
7.5 |
8.0 |
8.5 |
9.5 |
|
140 |
+1.7 0 |
0.6 |
- |
6.0 |
8.0 |
8.5 |
9.5 |
10.5 |
|
160 |
+2.0 0 |
0.6 |
- |
6.5 |
9.0 |
9.5 |
10.5 |
11.5 |
|
200 |
+2.3 0 |
0.6 |
- |
7.0 |
9.5 |
10.5 |
12.5 |
13.0 |
|
225 |
+2.5 0 |
0.6 |
- |
8.0 |
10.0 |
10.5 |
12.5 |
- |
|
250 |
+2.7 0 |
0.6 |
8.0 |
10.5 |
12.0 |
12.0 |
13.0 |
- |
|
315 |
+2.8 0 |
0.6 |
9.5 |
12.0 |
13.0 |
13.0 |
14.5 |
- |
|
355 |
+3.0 0 |
0.8 |
10.0 |
12.5 |
14.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
400 |
+3.2 0 |
0.8 |
10.5 |
13.0 |
15.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
450 |
+3.2 0 |
0.8 |
11.5 |
14.0 |
16.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
500 |
+3.2 0 |
0.8 |
12.5 |
16.0 |
18.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
560 |
+3.2 0 |
0.8 |
17.0 |
20.0 |
21.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
630 |
+3.2 0 |
0.8 |
20.0 |
22.0 |
24.0 |
- |
- |
- |
|
710 |
+3.8 0 |
1.0 |
23.0 |
26.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
800 |
+3.8 0 |
1.0 |
27.0 |
30.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Note: Products refer to the implementation of GB/T32439, CJ/T189, HG/T4586 national standards and industry standards |
||||||||
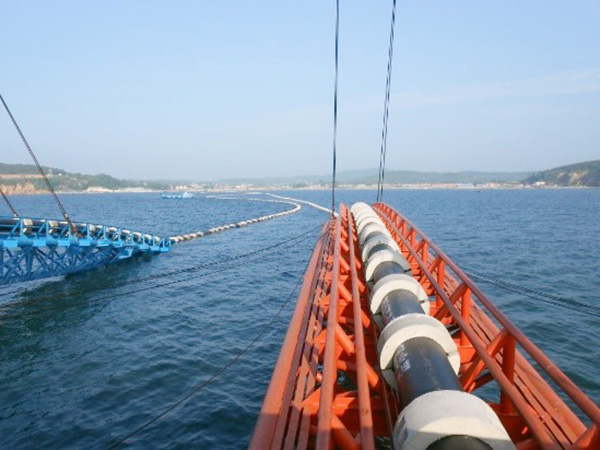
Product detail pictures:
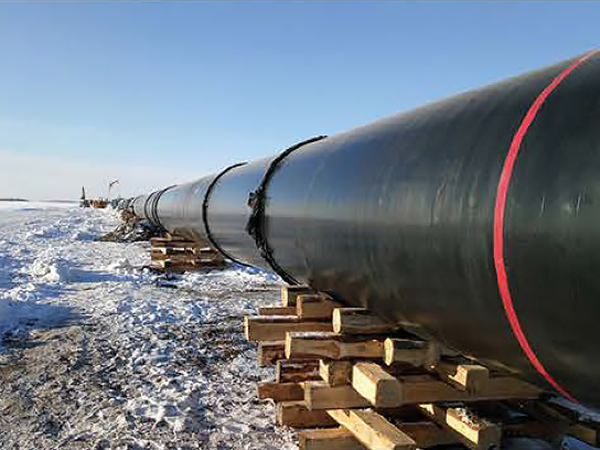
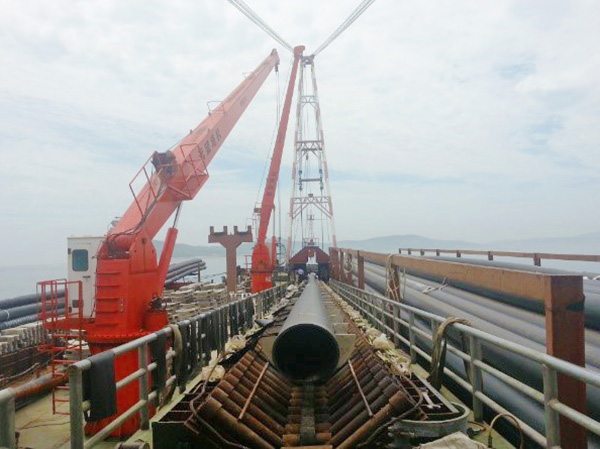
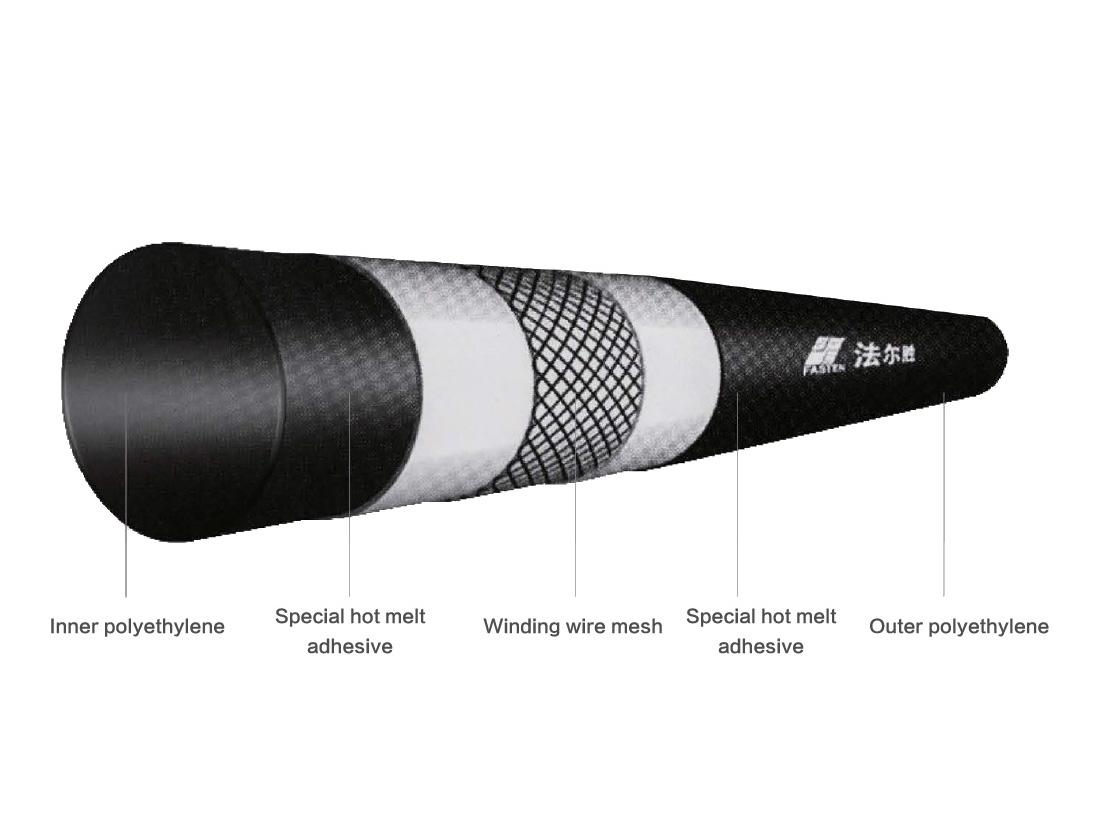






Related Product Guide:
We have quite a few great team customers very good at internet marketing, QC, and dealing with kinds of troublesome trouble while in the output approach for China New Product Phosphate Treatment For Steel Wire - Steel mesh skeleton polyethylene pipe – Fasten , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Lyon, Cologne, Salt Lake City, Our company insists on the purpose of "takes service priority for standard, quality guarantee for the brand, do business in good faith, to provide professional, rapid, accurate and timely service for you". We welcome old and new customers to negotiate with us. We will serve you with all sincerity!
Timely delivery, strict implementation of the contract provisions of the goods, encountered special circumstances, but also actively cooperate, a trustworthy company!








